Laser cladding
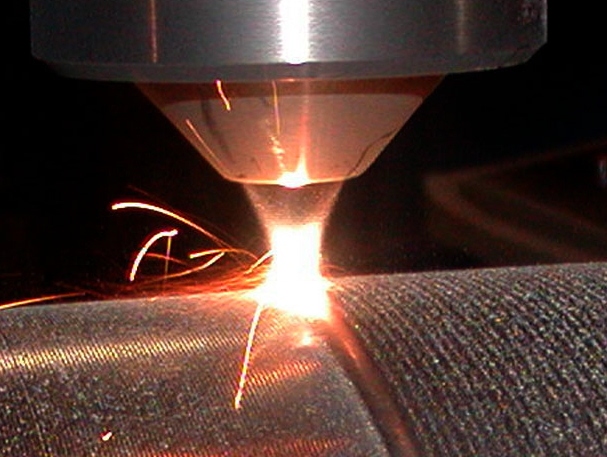
The laser deposition process (laser cladding) is an addition process of material on the surface of another in a controlled manner.
A defined thermal power is furnished by means of a laser source, focused on the melting point and moved on the surface to be coated by automatic control, by depositing the coating material.
The main advantages of this technique are:
- The possibility of depositing with extreme precision and localization new material with different features and characteristics with respect to the substrate;
- A wide range of couplings between different materials;
- Complete fusion of the coating and (theoretical) total absence of porosity;
- Minimization of thermal alteration and extension of the heat affected zone (HAZ), with direct advantages also on the distortions of the substrate and reduced need for subsequent machining;
- Easily automated and integrated CAD / CAM and CNC systems.
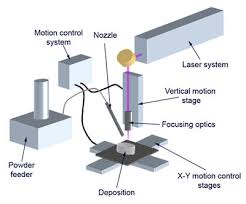
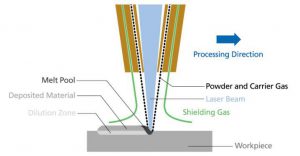
In case of the laser source, this process combines the advantages of the specific technology to the peculiar characteristics of the heat source, with further benefits represented by:
- Perfect metallurgical bond between the substrate and the coating material;
- Extremely fine and homogeneous microstructures, particularly suitable for wear and erosion-corrosion applications and to the use of engineered powders otherwise not be used with other welding technologies;
- High precision and final finish, minimal material intake, reduced need for finishing;
- Use in repair operations (repairing) and recovery (restoring) the broken and/or worn parts;
- More and more widely employed in additive manufacturing laser operations (DED processes and its derivatives).